5Ms of Geriatrics
Blog: November, 2025
Source: http://www.aginghealthforum.com/
5Ms OF GERIATRICS-ADVANCING TOWARDS AN AGE FRIENDLY HEALTH CARE SYSTEM
Much water has flown over the evolution of geriatric health care as a medical discipline. Term geriatrics to indicate Medicine of the old age was first proposed by Machnikov in 1908 and later in 1909 by Nascher who is known as father of geriatrics in the United States. It was in 1935 when the mother of geriatrics, Marjory Warren (1897-1960) established the roots of modern geriatrics in the United Kingdom. She demonstrated that chronically ill bed ridden elderly patients could also be successfully managed to gain some degree of independence and rehabilitation and could be discharged from the hospital. Bernard Issac’s description of four geriatric giants-impairment of intellect (cerebral dysfunction), incontinence, immobility and instability (falls) was another landmark as they lead to reduced activity levels and functional status during old age, resulting in reduced participation, independence, and involvement in everyday life.
Unlike younger subjects, elderly patients often have complex health issues like declining physical and mental capacities and socioeconomic problems resulting in loss of independence and poor quality of life in addition to having lifelong multiple comorbidities and disabilities. Many physicians of the day however ignored some of these problems and continued to provide traditional single disease specific management. This trend however slowly but surely began to change in the subsequent years when trained geriatric medicine practitioners started managing elderly patients for their unique health needs with a focus on a holistic approach of care to address the medical, psychological, social and spiritual aspects of ageing. In India, however, many general physicians, although not trained in geriatrics are still interested in treating elderly patients. Paradoxically, yet, there is some degree of professional and institutional aversion to the field of geriatrics as a career path, a phenomenon called geriatrism. It is hoped that with a rapidly burgeoning population of elderly persons and their evolving needs in consonance with advancing geriatric-related sub-fields like healthy ageing, community geriatrics, home care, care giving strategies, geriatric rehabilitation, institutionalisation, assistive living, day care, digital care, perioperative care, hospice, palliative and end of life care etc., geriatric medicine is set to be firmly on its feet.
Currently we are still confronted with challenges of providing tailored intervention strategies, understanding numerous assessment tools, approaching perplexing geriatric medication issues and adapting to new and evolving care models to deal with highly heterogenous and rapidly rising elderly population. No wonder, last half a century has witnessed several care and assessment models, notably comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA), home care, geriatric day hospital care, WHO’s integrated care for the older persons {ICOPE) etc., and more recently, the framework of 5Ms of geriatrics. Comprehensive geriatric assessment which examines physical, cognitive, affective, nutritive, social and environmental domains has been shown to improve outcomes for frail seniors in acute care and rehabilitation settings, and models of care involving geriatricians in family medicine have shown positive outcomes and patient and provider satisfaction. Home visits by geriatric outreach teams have also been shown to decrease mortality rates in patients aged 65 to 80 and to reduce nursing home admission rates. Geriatric day hospital care was associated with reduced death, reduced institutionalization, greater independence, and higher levels of physical function. ICOPE stresses on community approach by screening elderly persons for their intrinsic capacity (comprising of six specific domains-cognition, mobility, vitality, vision, hearing and psychology) and when required by providing intervention at primary, secondary and tertiary levels.
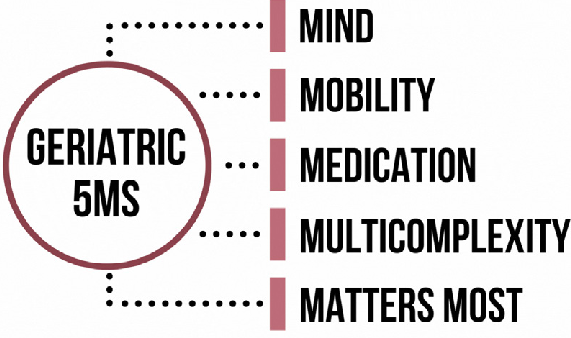
Under 5Ms, geriatric providers focus holistically on five under mentioned key areas to build an age friendly health care system.
MIND: Maintaining mental activity and dealing with dementia, depression and delirium.
MOBILITY: Maintaining ability to walk and balance and prevent falls and injuries.
MEDICATION: Prescribing only those medicines which are needed for the patient and creating awareness about the side effects of medicines.
MULTICOMPLEXITY: Helping patient manage a variety of health conditions and geriatric syndromes and assessing his living conditions including his social and financial state.
MATTERS MOST: Providing management to ensure health outcomes, goals and preferences that are personally meaningful to the elderly individual. Awareness is also needed about advance care planning (ACP) or living will without which, patient’s wishes might never be known or honoured. Elderly persons may value function over longevity, independence over intervention, and comfort over cure. In an Indian study by Priyadarshani, Ramya and Deepa from Chennai, issues that mattered most were connecting, functioning and enjoying life and that the older persons prioritized quality of life over longevity with strong emphasis on social connections and functional independence.
In view of prevailing scarcity of geriatricians that is not going to vanish in near future, different specialities and their individual health care providers have also to adopt 5Ms framework and pitch in with skills for comprehensive assessments of older adults, compassionate and personalized care and to generate safety and efficacy data for therapeutic agents and assess outcomes that are meaningful to their patients. Diabetology, gastroenterology, rheumatology, physical therapy, cardiology, oncology, dentistry, nursing, social work, and others are already delving in 4Ms or 5Ms approach. Primary care clinician to whom the elderly patient often makes the first contact should also become geriatric informed. These steps are likely to build a more robust age friendly health care system across different medical disciplines and across the country.
_20240725123207.jpg)